GOOGLE SEO TRAININGCERTIFICATION l FREE ONLINE SEO TRAINING EBOOK l SEO COURSE FOR BEGINNERS
 |
| FREE SEO COURSE CHAPTER 2 |
CHAPTER 1, STRATEGIC GOALS SEO PRACTITIONERS CAN FULFIL
— Visibility (Branding)
— Website Traffic
— High Return on Investment
CUSTOMIZED SEO STRATEGY
— What the organization is trying to
promote (service, product, content)
Who the target market is (can be as
simple as “women” or as detailed as personas)
— Brand (includes copy and messaging)
— Website structure (includes site
architecture, navigational elements, and file/URLnaming conventions)
— Current site content assets
(includes images, videos, PDF files, white papers, casestudies, articles)
— Ease with which the content and site
structure can be modified (involves the CMSand web development teams)
— Editorial resources and calendar for
content development (what content is developed,by whom, and on what timeline)
— Competitive landscape
UNDERSTANDING SEARCH ENGINE TRAFFIC & VISITOR INTENT
— These can generally be classified
into three major categories:
— Navigational query
— This is a query with the intent to
arrive at a specific website or page (e.g., the person types in your company
domain name, www.companyname.com, or simply types in the word facebook).
— Informational query
— This is a search performed to
receive an answer to a broad or direct question, or to research and explore
information around a specific topic with no specific source in mind (e.g., yoga
poses).
TRANSACTIONAL QUERY
— A person who types in digital camera
may be looking to buy one now, but it is equally possible that she is
researching digital cameras to learn about how they are different from film
cameras. This is an example of an initial transactional query, which can evolve
in stages. For example, here are some other types of transactional queries that
occur at a later stage in the buying cycle:
— The user types in best online
digital camera store. Although there is no information in the query about which
one she wants to buy, the intent is clearer that the searcher is seeking a
store, not simply information about types of digital cameras.
— The searcher types in olympus OMD
lowest price. The chances are very high thatthis user is looking to buy that
particular camera.
— Part of an SEO strategy is to
understand how the various types of searches relate to the content and
architecture of your website.
DEVELOPING AN SEO PLAN
— It is widely understood in the SEO
industry that SEO should be built in, as early as possible, to the entire site
development strategy—from choosing a content management system (CMS) and
planning site architecture to creating, optimizing, and publishing site
content. SEO plans have many moving parts, and SEO-related decisions can and
usually do have a significant impact on other departments, such as web
development, content development and editorial, other marketing groups (direct,
offline, etc.), and sales.
— Integrating these moving parts and
aligning them with each other is essential to developing an SEO-friendly
website and establishing a strong foundation for enduring organic visibility.
BUSINESS FACTORS THAT IMPACT YOUR SEO STRATEGY
— Revenue and business models
— The effective SEO strategy takes
into account the purpose of the site whether it is to sell products, sell
advertising, obtain leads, or gain membership signups.
— Target customers
— Who are you trying to reach? This
could be an age group, a gender group, or as specific as people looking to buy
a house within a specific neighbourhood of San Francisco, California.
— Competitors
— The competitive landscape is another
big factor in your overall strategy. Competition may be strongly entrenched in
one portion of the market online, and it may make sense to focus on a different
segment. Or you may be the current leader in your market and want to protect
this position while continuing to build your customer base.
— Branding goals
— There may be search terms for which
it is critical that you have top search exposure, for branding reasons.
— Content development
— An important part of SEO and general
online success is the creation and optimization of high-quality content for
your users. For most businesses, your capacity to create quality content on an
ongoing basis can significantly improve your SEO efforts, both from a
content-availability perspective (more content in the search engines) and from
a user engagement and link development perspective (great
— content breeds great links and
social sharing, both of which can positively influence SEO).
— How people search for products like
yours
— Understanding what customers do when
they are searching for products or services like yours is one of the most basic
functions of SEO,
UNDERSTANDING YOUR AUDIENCE & FINDING YOUR NICHE
•
Mapping
Your Products and Services
•
Understanding That Content Is King
•
Segmenting Your Site’s Audience
•
Understanding Context: Market Competitiveness
SEO FOR RAW TRAFFIC
— Use it when you can monetize traffic
without actions or financial transactions taking place on your site (usually
through advertising).
— Keyword targeting
— Keyword targeting in this scenario
can be very broad. The goal here isn’t typically to select specific keywords,
but rather to create high-quality content that naturally targets interesting,
searched-for terms.
— Instead of singular optimization on
specific terms, the focus is on accessibility and best practices throughout the
site to earn traffic through both high-volume and long-tail queries
— Concentrate efforts on great
content, and use keyword based optimization as a subsequent application to
confirm the titles, headlines, filenames, metadata, and other elements of the
content you create.
— Page and content
creation/optimization
— A shallow, highly crawl able link
structure is critical to getting all of your content indexed—follow good
information architecture practices and use intelligent, detailed category and
subcategory structures to get the most benefit out of your work. You’ll also
need to employ good on-page optimization in <title> tags, headlines,
internal links, and so on, and make your articles easy to share and optimized
for viral spreading
DEVELOPMENT PLATFORM AND INFORMATION ARCHITECTURE
— Technology Decisions
— Structural Decisions
Technology Decisions
— SEO is a technical process, and as
such, it impacts major technology choices. For example, a CMS can facilitate
(or possibly undermine) your SEO strategy: some platforms do not allow you to
write customized titles and meta descriptions that vary from one web page to
the next, while some create hundreds (or thousands) of pages of duplicate
content (not good for SEO!).
Dynamic URLs
— Dynamic URLs are URLs for dynamic
web pages (which have content generated "on the fly” by user requests).
These URLs are generated in real time as the result of specific queries to a
site’s database—for example, a search for leather bag on Etsy results in
the dynamic search result URL https://www.etsy.com/search?q=leather
%20bag. However, Etsy also has a static URL for a static page showing leather
bags at https://www.etsy.com/market/leather_bag.
— Although Google has stated for some
time that dynamic URLs are not a problem for the search engine to crawl, it is
wise to make sure your dynamic URLs are not “running wild” by checking that
your CMS does not render your pages on URLs with too many convoluted
parameters. In addition, be sure to make proper use of
rel="canonical", as outlined by Google (http://bit.ly/canonical_urls).
— Finally, while dynamic URLs are
crawl able, don’t overlook the value of static URLs for the purpose of
controlling your URL structure for brevity, descriptiveness, user-friendliness,
and ease of sharing.
Session IDs or user IDs in the URL
— It used to be very common for a CMS
to track individual users surfing a site by adding a tracking code to the end
of the URL. Although this worked well for this purpose, it was not good for
search engines, because they saw each URL as a different page rather than a
variant of the same page. Make sure your CMS does not ever serve up session
IDs.
LINKS OR CONTENT BASED IN FLASH
— Search engines often cannot see
links and content implemented with Flash technology. Have a plan to expose your
links and content in simple HTML text, and be aware of Flash’s limitations.
CONTENT BEHIND FORMS (INCLUDING PULL-DOWN LISTS)
— Making content accessible only after
the user has completed a form (such as a login) or made a selection from an
improperly implemented pull-down list is a great way to hide content from the
search engines. Do not use these techniques unless you want to hide your
content!
TEMPORARY (302) REDIRECTS
This is also a common problem in web server
platforms and content management systems. The 302 redirect blocks a search
engine from recognizing that you have permanently moved the content, and it can
be very problematic for SEO, as 302 redirects block the passing of PageRank.
Make sure the default redirect your systems use is a 301
STRUCTURAL DECISIONS
— What pages are linked to from the
home page? What pages are used as top-level categories that then lead site
visitors to other related pages? Do pages that are relevant to each other link
to each other? There are many, many aspects to determining a linking structure
for a site, and it is a major usability issue because visitors make use of the
links to surf around your website. For search engines, the navigation structure
helps their crawlers determine what pages you consider the most important on
your site, and it helps them establish the relevance of the pages on your site
to specific topics.
TARGET KEYWORDS
— Keyword research is a critical
component of SEO. What search terms do people use when searching for products
or services similar to yours? How do those terms match up with your site
hierarchy? Ultimately, the logical structure of your pages should match up with
the way users think about products and services like yours.
 |
| Targeted Keywords |
CROSS-LINK RELEVANT CONTENT
— Linking between articles that cover
related material can be very powerful. It helps the search engine ascertain
with greater confidence how relevant a web page is to a particular topic. This
can be extremely difficult to do well if you have a massive ecommerce site, but
Amazon handles it nicely, as shown in Figure
 |
| Cross Link Relevant Content |
— The “Frequently Bought Together” and
“Customers Who Bought This Item Also Bought” sections are brilliant ways to
group products into categories that establish the relevance of the page to
certain topic areas, as well as to create links between relevant pages.
— In the Amazon system, all of this is
rendered on the page dynamically, so it requires little day-to-day effort on
Amazon’s part. The “Customers Who Bought...” data is part of Amazon’s internal
databases, and the “Tags Customers Associate...” data is provided directly by
the users themselves.
— Of course, your site may be quite
different, but the lesson is the same: you want to plan on having a site
architecture that will allow you to cross-link related items.
USE ANCHOR TEXT, INTUITIVELY
— Anchor text has generally been one
of the golden opportunities of internal linking, and exact-match keyword anchor
text was generally the protocol for internal linking for many years. However,
in these days of aggressive anchor text abuse (and crackdown by the search
engines), while keyword-infused anchor text in internal links is still often
the most intuitive and user-friendly, we generally advocate for a more
broad-minded approach to crafting internal anchor text. Use descriptive text in
your internal links and avoid using irrelevant text such as “More” or “Click
here.” Try to be. as specific and contextually relevant as possible and include
phrases when appropriate within your link text. For example, as a crystal
vendor, you might use “some of our finest quartz specimens” as anchor text for
an internal link, versus “quality quartz crystals.” Make sure that the
technical, creative, and editorial teams understand this approach, as it will
impact how content is created, published, and linked to within your site.
USE BREADCRUMB NAVIGATION
— Breadcrumb navigation is a way to
show the user where he is in the navigation hierarchy. Figure shows an example
from PetSmart. This page is currently four levels down from the home page.
Also, note how the anchor text in the breadcrumb is keyword-rich, as is the
menu navigation on the left. This is helpful to both users and search engines.
 |
| Use Breadcrumb Navigation |
MINIMIZE LINK DEPTH
— Search engines (and people) look to
the site architecture for clues as to what pages are most important. A key
measurement is how many clicks from the home page it takes a person, and a
search engine crawler, to reach a page. A page that is only one click from the
home page is clearly important, while a page that is five or six clicks away is
not nearly as influential. In fact, the search engine spider may never even
find such a page, depending in part on the site’s link authority.
— Standard SEO advice is to keep the
site architecture as flat as possible, to minimize clicks from the home page to
important content. The bottom line is that you need to plan out a site
structure that is as flat as you can reasonably make it without compromising
your user experience.
— In this and the preceding sections,
we outlined common structural decisions that you need to incorporate into your
SEO strategy prior to implementation. There are other considerations, such as
how to make your efforts scale across a very large site (thousands of pages or
more). In such a situation, you cannot feasibly review every page one by one.
MOBILE SITES AND MOBILE APPS
— If you are building a website, you
need to build a mobile version if you want to take full advantage of organic
search through SEO—and depending on your business, you may benefit from
developing a mobile app as well. The main consideration regarding your site’s
mobile version is whether to host it on the same or separate URLs as your
desktop version—and, if you’re utilizing the same URLs, whether to choose
responsive design or dynamic serving (a.k.a. adaptive design).
SINGLE-PAGE APPLICATIONS
— Single-page applications (SPAs) are
web applications that use AJAX and HTML5 to load a single HTML page in a web
browser, and then dynamically update that page’s content as the user interacts
with the app. The majority of the work in loading page content, or rendering,
is done on the client side (as opposed to the server side), which makes for
a fast and fluid user experience and minimized page loads, often while the page
URL remains the same. Commonly used frameworks for SPA development include
Angular.js, Backbone.js, and Ember.js, which are used by many popular
applications including Virgin America, Twitter, and Square, respectively. One
of the main issues to address when you’re building a site with one of these
frameworks is URL crawlability—namely, ensuring that the search engines can
crawl your site’s URLs to access your site content. It is important that
you have a publishing system that allows you to customize URLs to remove the #
or #! (hashbang) from the URL, and to create user-friendly, bookmarkable,
back-clickable URLs. There are various methods that developers can use to
implement search- and user-friendly URLs, with the two most recent being
window.location.hash and HTML5’s history.pushState—both of which have
advantages and disadvantages depending on your site and user objectives.
AUDITING-ELEMENTS OF AN AUDIT
— Page load time
— Is the page load time excessive? Too
long a load time may slow down crawling and indexing of the site, and can
virtually eliminate your site from competitiveness in mobile search.
— Mobile-friendliness
— Your site should have a fast,
mobile-friendly version that is served to mobile devices.
— Usability
— Usability affects many factors,
including conversion rate as well as the propensity of people to link to a
site.
— Accessibility/Spider ability
—
Make sure
the site is friendly to search engine spiders.
— Duplicate content checks
— The first thing you should do is
make sure the non-www versions of your pages (i.e., http://yourdomain.com)
301-redirect to the www versions (i.e., http://www.yourdomain.com), or vice
versa (this is often called the canonical redirect). While you are at it,
— check that you don’t have https:
pages that are duplicates of your http: pages. You should check the rest of the
content on the site as well.
— The easiest way to do this is to
take unique text sections from each of the major content pages on the site and
search on them in Google. Make sure you enclose the string inside double quotes
(e.g., “a phrase from your website that you are using to check for duplicate
content”) so that Google will search for that exact string. If you see more
than one link showing in the results, look closely at the URLs and pages to
determine why it is happening.
— URL checks
— Make sure you have clean, short,
descriptive URLs. Descriptive means keyword-rich but not keyword-stuffed
(e.g., site.com/outerwear/mens/hats is keyword-rich;
site.com/outerwear/mens/hat-hats-hats-for-men is keyword-stuffed!). You don’t
want parameters appended (have a minimal number if you must have any), and
you want them to be simple and easy for users (and search engine spiders) to
understand.
HTML <TITLE> TAG REVIEW
— Make sure the <title> tag on
each page of the site is unique and descriptive. If you
— want to include your company brand
name in the title, consider putting it at the end
— of the <title> tag, not at the
beginning, as placing keywords at the front of a page title
— (generally referred to as prominence)
brings ranking benefits. Also check to ensure the
— <title> tag is fewer than 70
characters long, or 512 pixels wide.
CONTENT REVIEW
— Do the main pages of the site have
enough text content to engage and satisfy a site visitor? Do these pages all
make use of header tags? A subtler variation of this is making sure the number
of pages with little content on the site is not too high compared to the total
number of pages on the site.
META TAG REVIEW
— make sure every page has a unique
meta description. If for some reason that is not possible, consider removing the
meta description altogether. Although the meta description tags are generally
not a direct factor in ranking, they may well be used in duplicate content
calculations, and the search engines frequently use them as the description for
your web page in the SERPs; therefore, they can affect click-though rate.
VERIFICATION
— Use the Google Search Console
“Robots.txt fetch” to check your robots.txt file. Also verify that your
Sitemap file is correctly identifying all of your site pages.
URL REDIRECT CHECKS
— Check all redirects to make sure the
right redirect is in place, and it is pointing to the correct destination URL.
This also includes checking that the canonical redirect is properly
implemented.
INTERNAL LINKING CHECKS
— Look for pages that have excessive
links. As discussed earlier, make sure the site makes intelligent use of anchor
text in its internal links. This is a user-friendly opportunity to inform users
and search engines what the various pages of your site are about. Don’t abuse
it, though. For example, if you have a link to your home page in your global
navigation (which you should), call it “Home” instead of picking your juiciest
key-word. The search engines can view that particular practice as spammy, and
it does not engender a good user experience.
EXTERNAL LINKING
— Check the inbound links to the site
by performing a backlink analysis. Use a backlinking tool such as
LinkResearchTools, Open Site Explorer, Majestic SEO, or Ahrefs Site Explorer
& Backlink Checker to collect data about your links. Look for bad patterns
in the anchor text, such as 87% of the links having the critical keyword for
the site in them. Unless the critical keyword happens to also be the name of
the company, this is a sure sign of trouble. This type of distribution is quite
likely the result of link purchasing or other manipulative behavior, and will
(if it hasn’t already) likely earn you a manual Google penalty or trigger
Google’s Penguin algorithm to lower your rankings.
— On the flip side, make sure the
site’s critical topics and keywords are showing up sometimes. A lack of the
topically related anchor text is not entirely good, either. You need to find a
balance, and err on the side of caution, intuitiveness, and usability.
IMAGE ALT ATTRIBUTES
— Do all the images have relevant,
keyword-rich alt attribute text and filenames? Search engines can’t easily tell
what is inside an image, and the best way to provide them with some clues is
with the alt attribute and the filename of the image. These can also reinforce
the overall context of the page itself.
CODE QUALITY
— checking the code itself is a good
idea (you can check it with the W3C validator. Poor coding can have some
undesirable impacts. You can use a tool such as SEO Browser to see how the
search engines see the page.
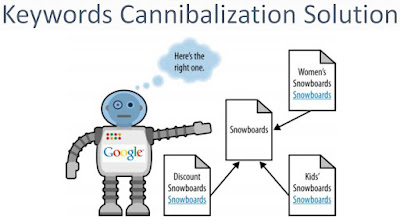
KEYWORD CANNIBALIZATION
— Keyword cannibalization typically
starts when a website’s information architecture calls for the targeting of a
single term or phrase on multiple pages of the site. This is often done
unintentionally, but it can result in several or even dozens of pages that have
the same keyword target in the title and header tags. Figure shows the problem.
 |
| Keyword Cannibalization |
 |
| Keyword Cannibalization |
IDENTIFYING CURRENT SERVER STATISTICS SOFTWARE & GAINING ACCESS
— Web Analytics
— Analytics software can provide you
with a rich array of valuable data about what is taking place on your site. It
can answer questions such as:
— How many unique visitors did you
receive yesterday?
— Is traffic trending up or down?
— What site content is attracting the
most visitors from organic search?
— What are the best-converting pages
on the site?
— It is strongly recommended that if
your site does not currently have any measurement systems in place, you remedy
that immediately. High-quality, free analytics tools are available, such as the
powerful and robust Google Analytics, as well as the open source platform
Piwik.


No comments:
Post a Comment